We use structural biology to study at atomic level how Immuno-Super-Molecular Machines work in respond to infection and cancer
Our research
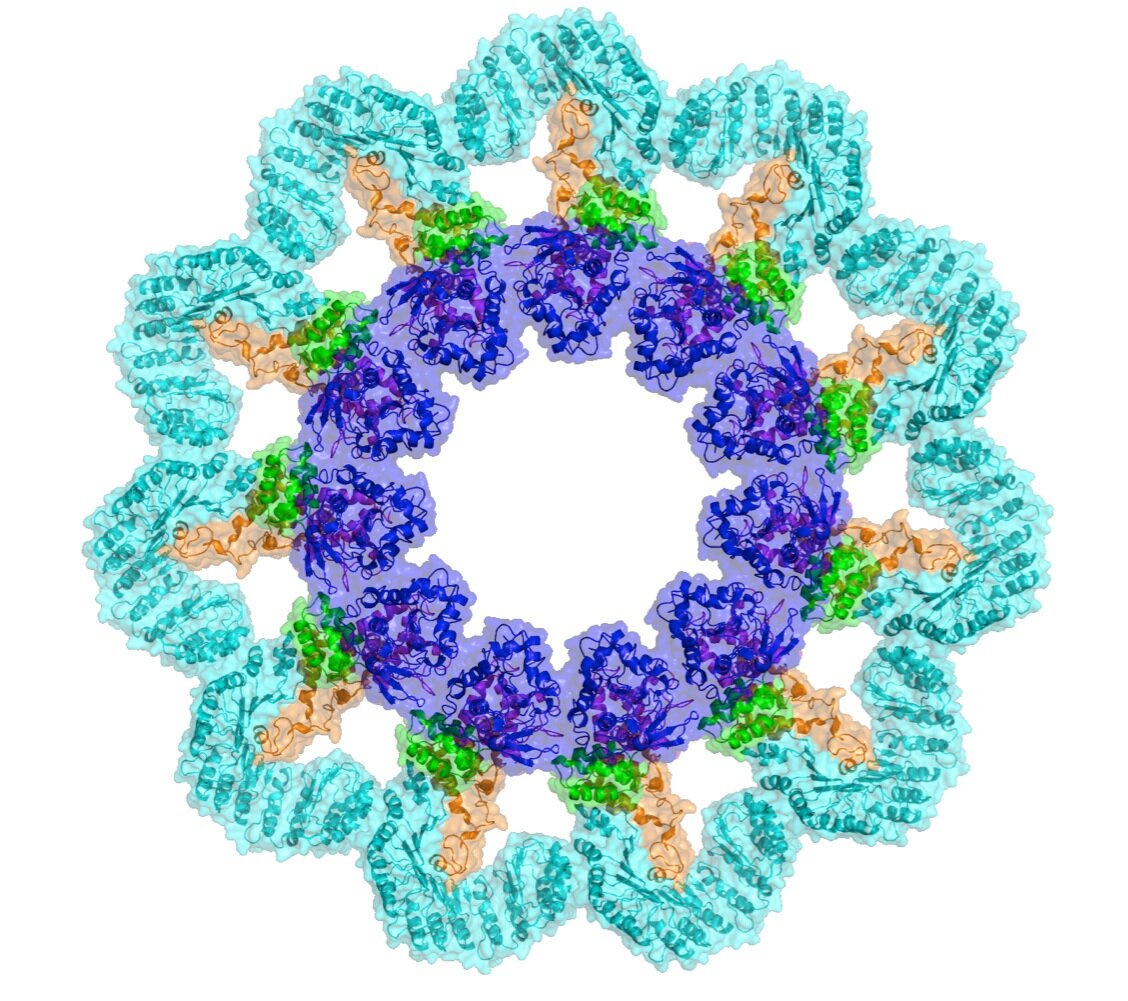
Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine rich repeat containing (NLR) proteins comprise a fascinating family that plays key roles in regulating immune signal transduction: they initiate inflammation in response to pathogens and danger signals by forming the NLR inflammasomes, restrict inflammation and anti-viral pathways through NLR inhibitors, and control MHC gene transcription. We aim to address the structural basis behind these functions, hope to provide fundamental knowledge that enables therapeutic applications to treat inflammatory diseases, immunodeficiency disorders, and cancer.
The techniques
crystallography
cryo-EM
biochemical and biophysical approaches
